It is important for businesses to regularly conduct CVP analysis and adjust their strategies accordingly to stay competitive and maximize profits. If the company were to increase the sales price of its widgets to $12, the contribution margin would increase to $7 per widget. This means that for every widget sold, the company would have a contribution margin of $7, which is $2 higher than its current contribution margin of $5. The additional $5 per unit in unit selling price adds 7% to the contribution margin ratio.
Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis and Contribution Margin
Regardless of the store’s sales volume, the fixed costs remain constant. In either case, the assumed costrelationships would no longer be valid. The difference between total sales revenue and total variable costs, representing the portion of sales that helps to cover fixed costs.
Create a Free Account and Ask Any Financial Question
It is a subset of CVP analysis focused on finding a situation where total revenue equals total costs, resulting in zero profit or loss. However, we will likely need to enter a sales dollar figure (rather than the number of units sold) on the register. This involves dividing the fixed costs by the contribution margin ratio.
Relationship Between Actual Costs & FP&A in Manufacturing
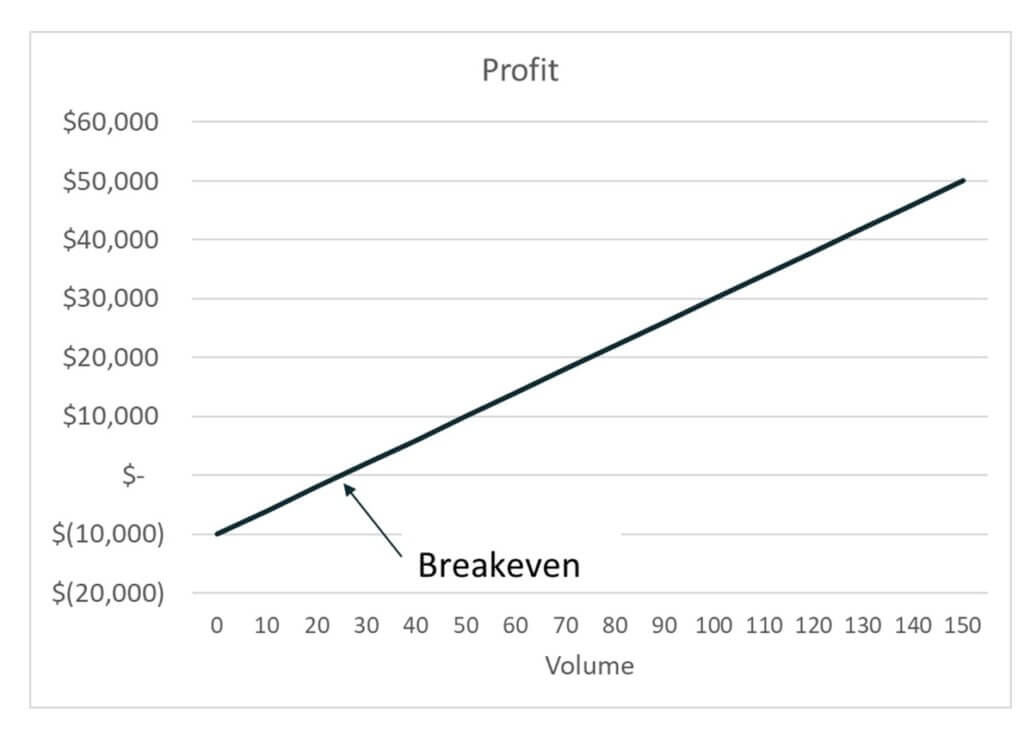
In conclusion, Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis is essential for businesses to understand their profit structure and make informed decisions to maximize profits. CVP analysis can be used to make informed decisions about pricing, product mix, and resource allocation. Break-even analysis is also used in cost/profit analyses to verify how much incremental sales (or revenue) is needed to justify new investments. CVP Analysis helps them to BEP Formula for different sales volume and cost structures. Fixed costs are unlikely to stay constant as output increases beyond a certain range of activity. The above graph shows the break-even point is between 2000 and 3000 units sold.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
The total revenue line represents the cumulative income an organization generates at various sales volume levels. It typically slopes upward linearly, reflecting the direct relationship between sales and revenue. Break-even points, where total costs equal total revenue, are also identified. Beyond this point, it illustrates profit zones, where revenue surpasses costs, and loss zones, where costs exceed revenue. Cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis is a method of evaluating the impact that varying levels of costs and volume have on a company’s operating profit. Cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis is a technique used to determine the effects of changes in an organization’s sales volume on its costs, revenue, and profit.
How Is Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis Used?
For example, the company could use CVP analysis to determine the impact of a price increase on its profits or to decide whether to produce and sell a new product line. Understanding variable costs is essential for conducting CVP analysis and for making informed decisions that maximize profits. We have introduced a new term in this incomestatement—the contribution margin. The contributionmargin is the amount by which revenue exceeds the variablecosts of producing that revenue.
The focus may be on a single product or on a sales mix of two or more different products. For example, if unit selling prices, unit variable costs, and total fixed costs remain constant, the P/V graph can show how many units must be sold to achieve a target profit. Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) analysis is a managerial accounting technique which studies the effect of sales volume and product costs on operating profit of a business. It shows how operating profit is affected by changes in variable costs, fixed costs, selling price per unit and the sales mix of two or more products. Cost Volume Profit (CVP) analysis is used in cost accounting to determine how a company’s profits are affected by changes in sales volume, fixed costs, and variable costs.
By keeping these watch-outs in mind, accountants can perform accurate and reliable CVP analysis and make informed decisions about pricing, product mix, and resource allocation. By gathering and analyzing this information, accountants can perform CVP analysis and make informed decisions about pricing, 3 important tax dates you need to know for 2016 product mix, and resource allocation. Accountants need to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data they use in their analyses to ensure that their conclusions are sound and reliable. Costs that do not change with the level of production or sales volume, such as rent, salaries, and insurance.
- Cost Volume Profit (CVP) analysis is used in cost accounting to determine how a company’s profits are affected by changes in sales volume, fixed costs, and variable costs.
- In more advanced treatments and practice, costs and revenue are nonlinear, and the analysis is more complicated, but the intuition afforded by linear CVP remains basic and useful.
- In the chart, wedemonstrate the effect of volume on revenue, costs, and net income,for a particular price, variable cost per unit, and fixed cost perperiod.
- Semi-variable expenses must be split between expense classifications using the high-low method, scatter plot, or statistical regression.
- This is where the magic happens a curve that combines the total revenue and total cost lines.
Learn how to run multiple regressions in Excel to analyze variable interactions, identify patterns, & enhance predictions. Data Consolidation in Excel simplifies handling multiple data sources, creating organized summaries that ease analysis, reduce errors, & support better insights. ChartExpo enhances the CVP chart by incorporating dynamic features like real-time data updates. This, as a result, facilitates adaptability to changing market conditions. Additionally, the user-friendly interface ensures accessibility for professionals across diverse sectors, fostering informed decision-making.



Comentarios recientes